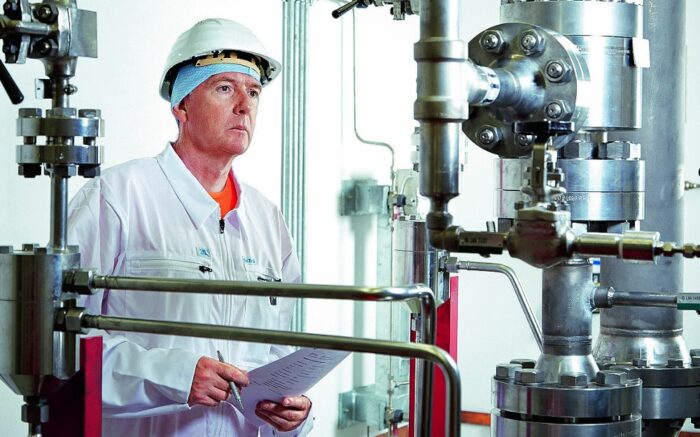
Ionising radiation can affect living organisms and cause damage to the organism, irrespective of whether the radiation is of natural or artificial origin. The severity of the effects depends on the energy absorbed by the cells and the duration of the exposure to radiation. When a person is exposed to a radiation field, the radiation acts on the body by releasing its energy into the body: We say that the person has an accumulated dose (cumulative). Doses are expressed in grays or sieverts.
Radiation biology is concerned with the effects of ionising radiation on humans, animals, plants and all other living organisms. By contrast, in epidemiology, statistical approaches are used to calculate the health risk resulting from radiation exposure.
The effects of radiation emitted by radioactive substances are widely known. Even at low doses, a correlation between the radiation dose and the probability of resultant illnesses is assumed. At low radiation doses, we refer to stochastic or random effects that can be calculated using statistical approaches. Higher radiation doses result in clinically observable effects in the body, e.g. to a loss of function in the affected organ. In this respect, the following applies: The higher the dose, the higher the severity of the resultant radiation sickness. Such effects are referred to as deterministic effects.
Further Information
- Article series «Radiation Biology»